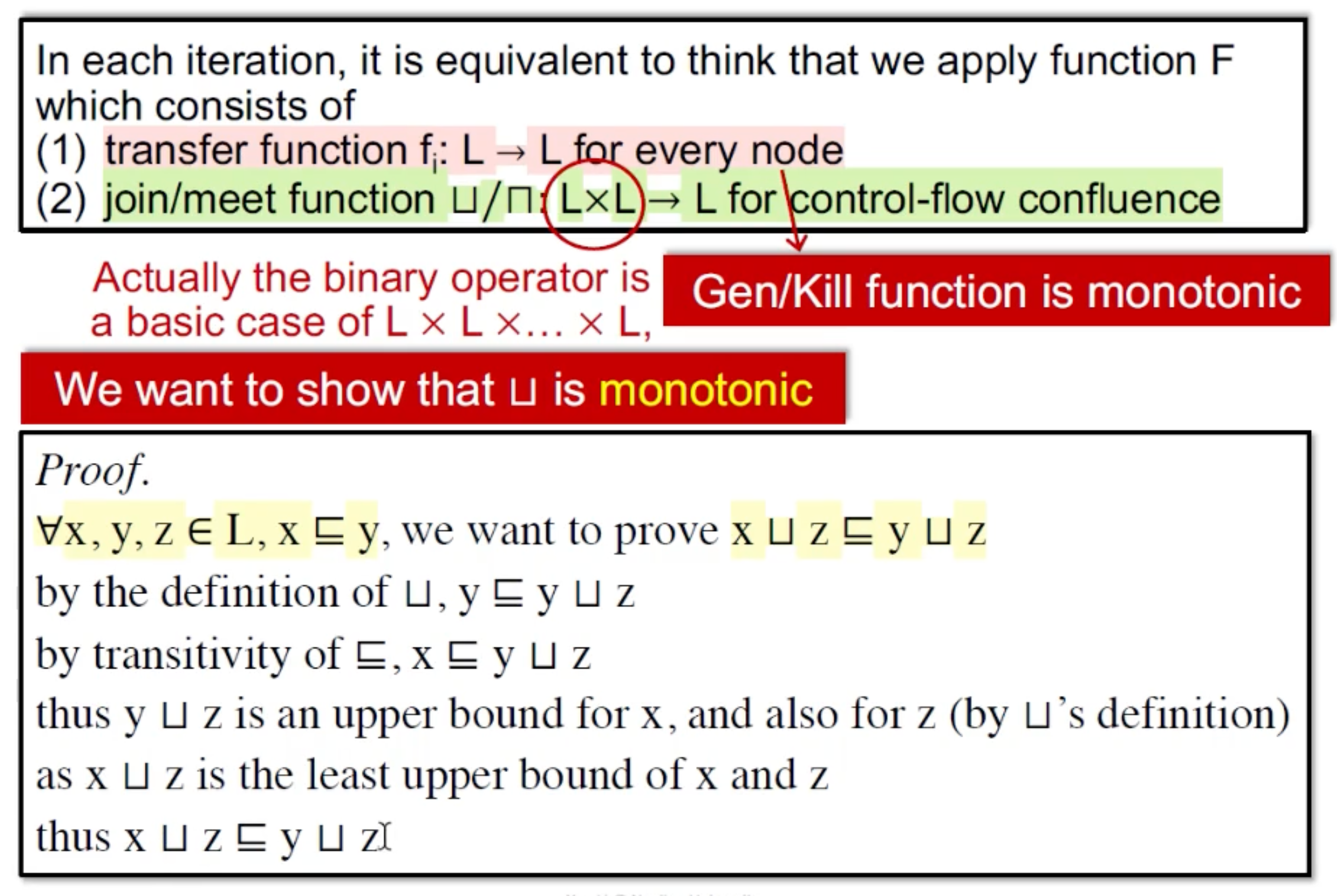
Relate Iterative Algorithm to Fixed-Point Theorem
不动点理论的前提是: 1. f: L → L是单调的 2. L是有限的。
如果可以将数据流分析问题映射到不动点理论中,则可以证明分析算法的收敛性。
对于数据流分析来说,每个节点的output是在有限值域中的,每个都是一个Lattice,整个程序是多个finite lattice的笛卡尔积,也是一个finite lattice。因此条件2满足。
然后需要证明数据流分析算法(1. transfer function, 2.join/meet on control flow)的单调性:
Q3: When will the Algorithm Reach the Fixed Point?
从Lattice的top→bottom的最长路径,称为lattice的height。
最坏情况下,每次迭代只有一个node在其lattice上走一步,假设CFG中k个node,每个node的lattice高度为h,那么总共需要k*h次迭代才能达到不动点。
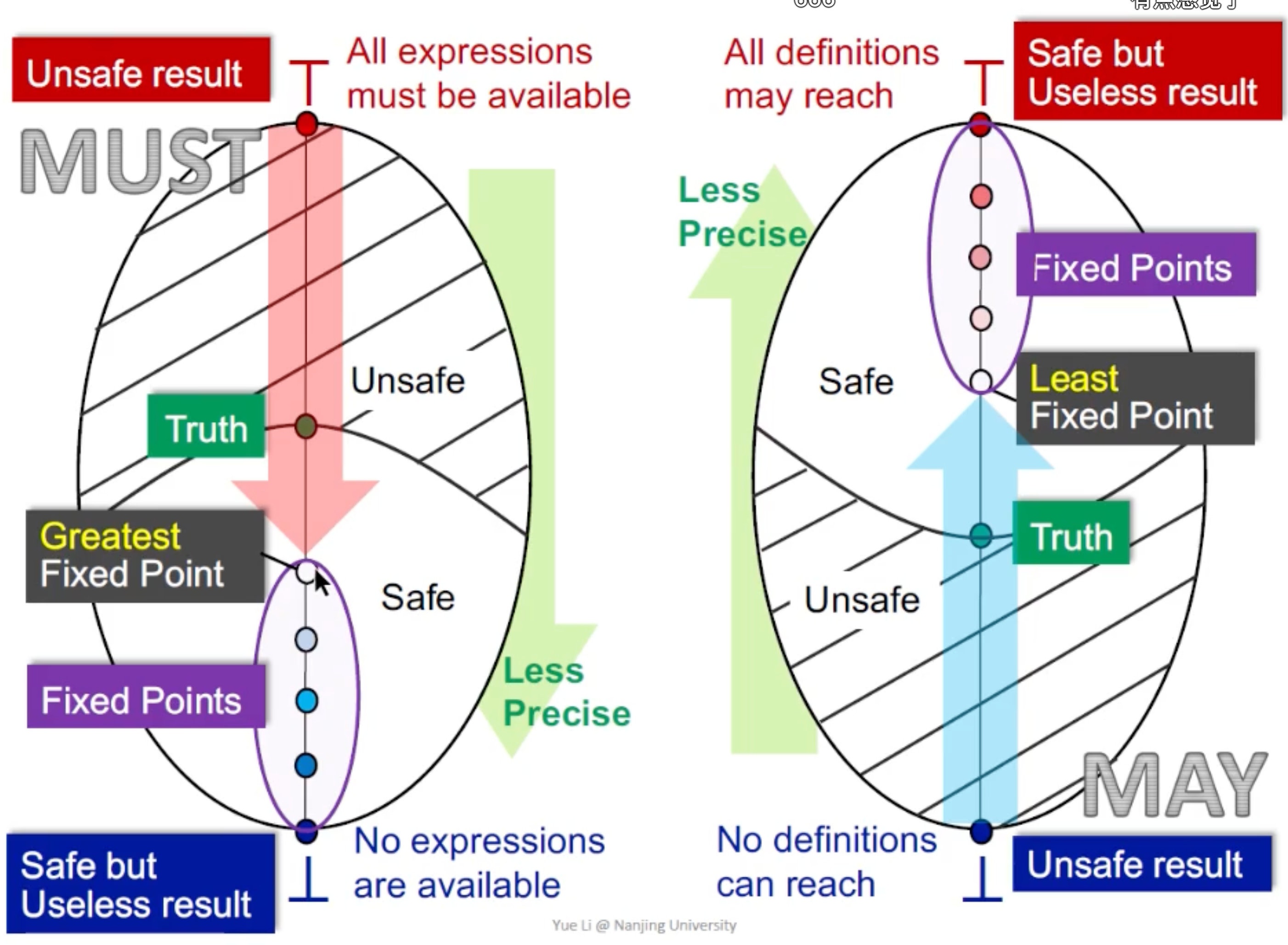
May and Must Analyses, a Lattice View
May和Must分析的应用场景不同,May-analysis一般用于寻找”可能”的错误,而Must-analysis一般用于寻找”一定存在”的错误。所以unsafe和safe的定义不同。
How Precise Is Our Solution?
Meet-Over-All-Paths Solution (MOP)
MOP[] = / (OUT[Entry]), path P from Entry to
该方法存在的问题:
Some paths may be not executable → not precise.
Unbounded or not enumerable paths → impractical.
把MOP结果当成一个precision metric. 和迭代算法的区别在与merge的顺序,即用了分配率的形式:
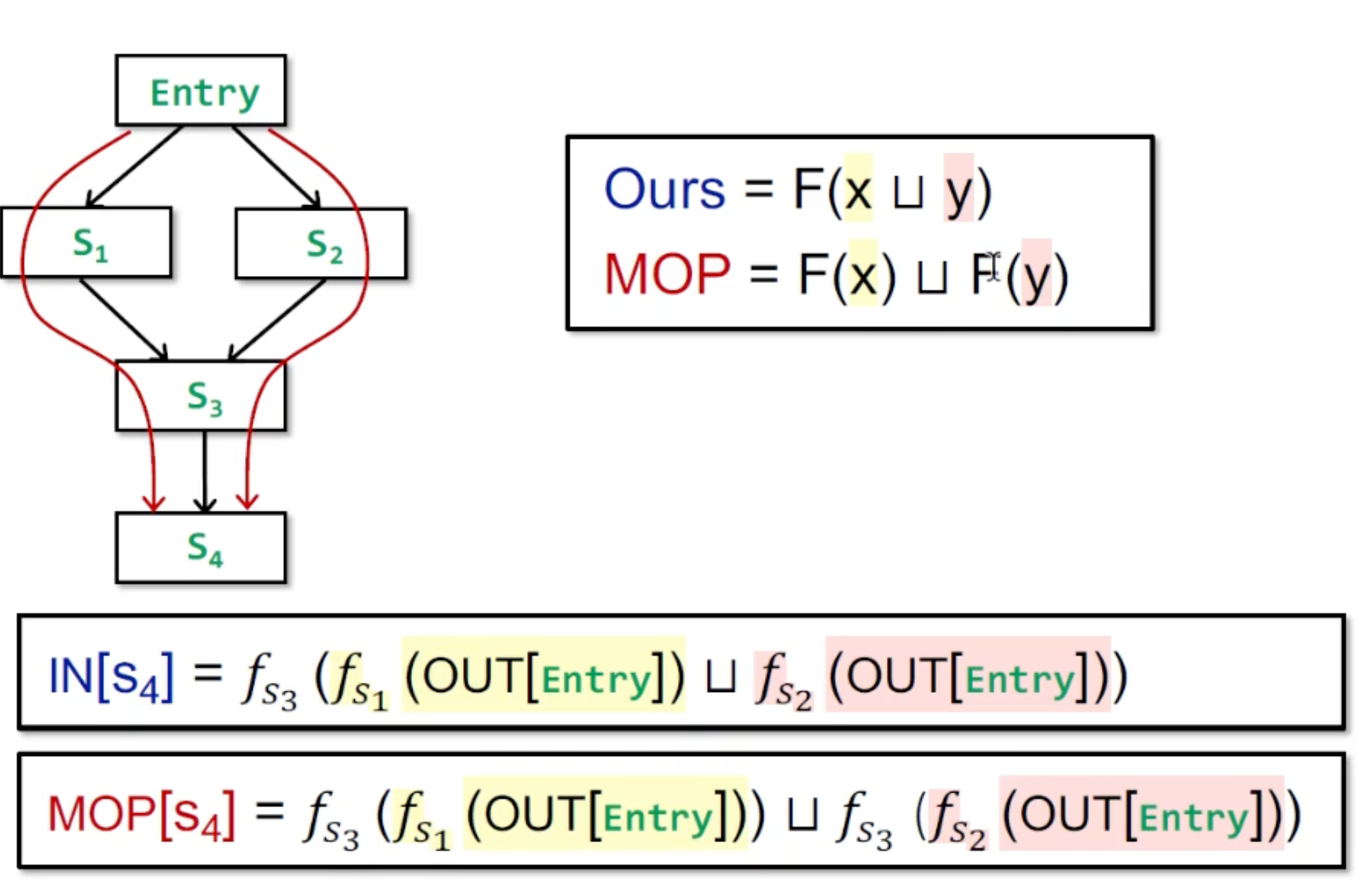
可以推出MOP其实是迭代算法的precision上界: F(x) F(y) F(x y), MOP 迭代算法。
原因是在这个例子的lattice上越往上越不准。当F可分配时,二者一样准。
之前遇到的所有Gen/kill问题都是F可分配的。
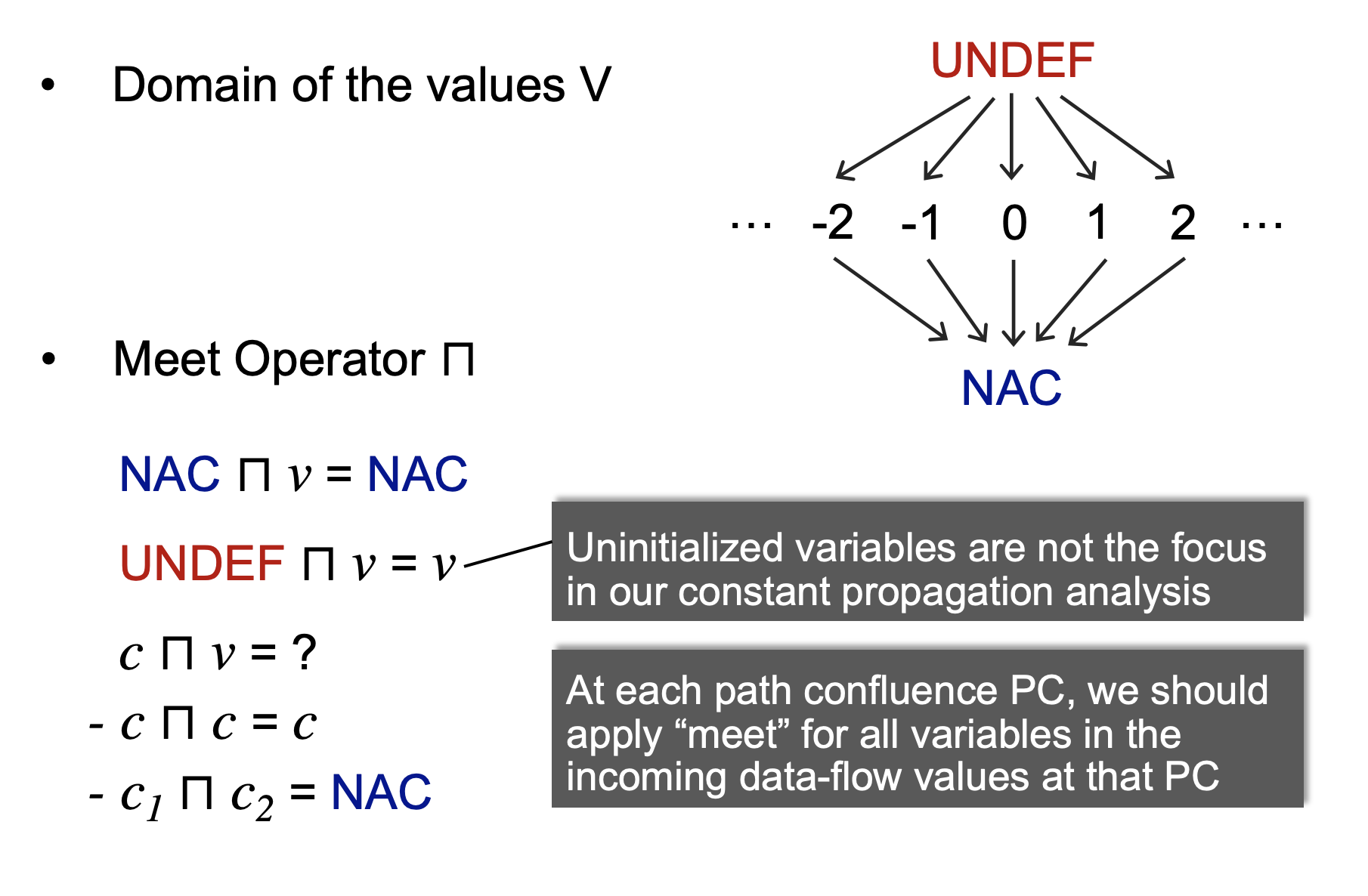
Constant Propogation (non-distributive)
定义: Given a variable x at program point p, determine whether x is guaranteed to hold a constant value at p
A Must-analysis.
1.映射到Lattice, 2. Meet operator :
3.Transfer Function:
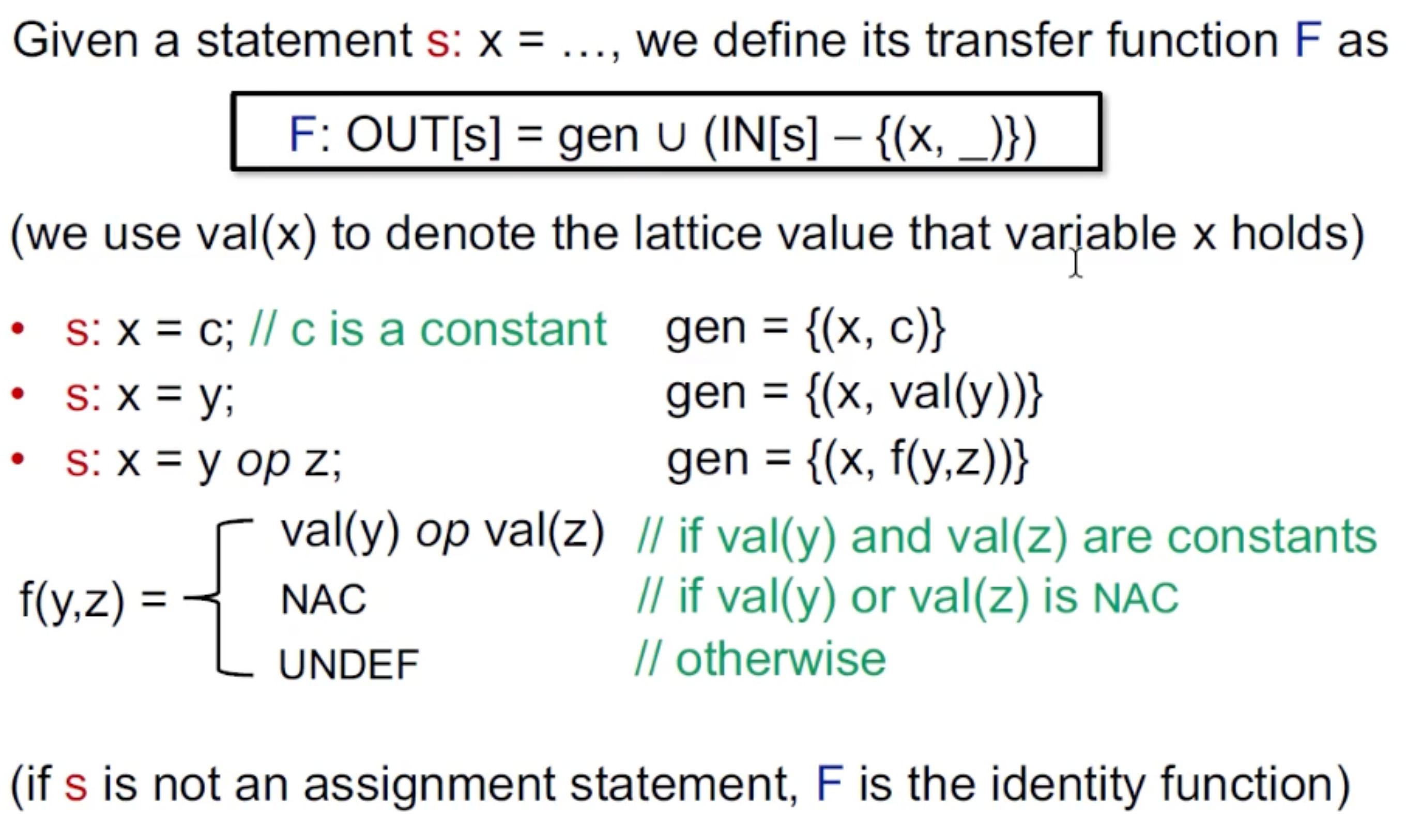
这个function就不是单调的了,因为otherwise的情况可能直接就回到top了。
non-distributive的例子:
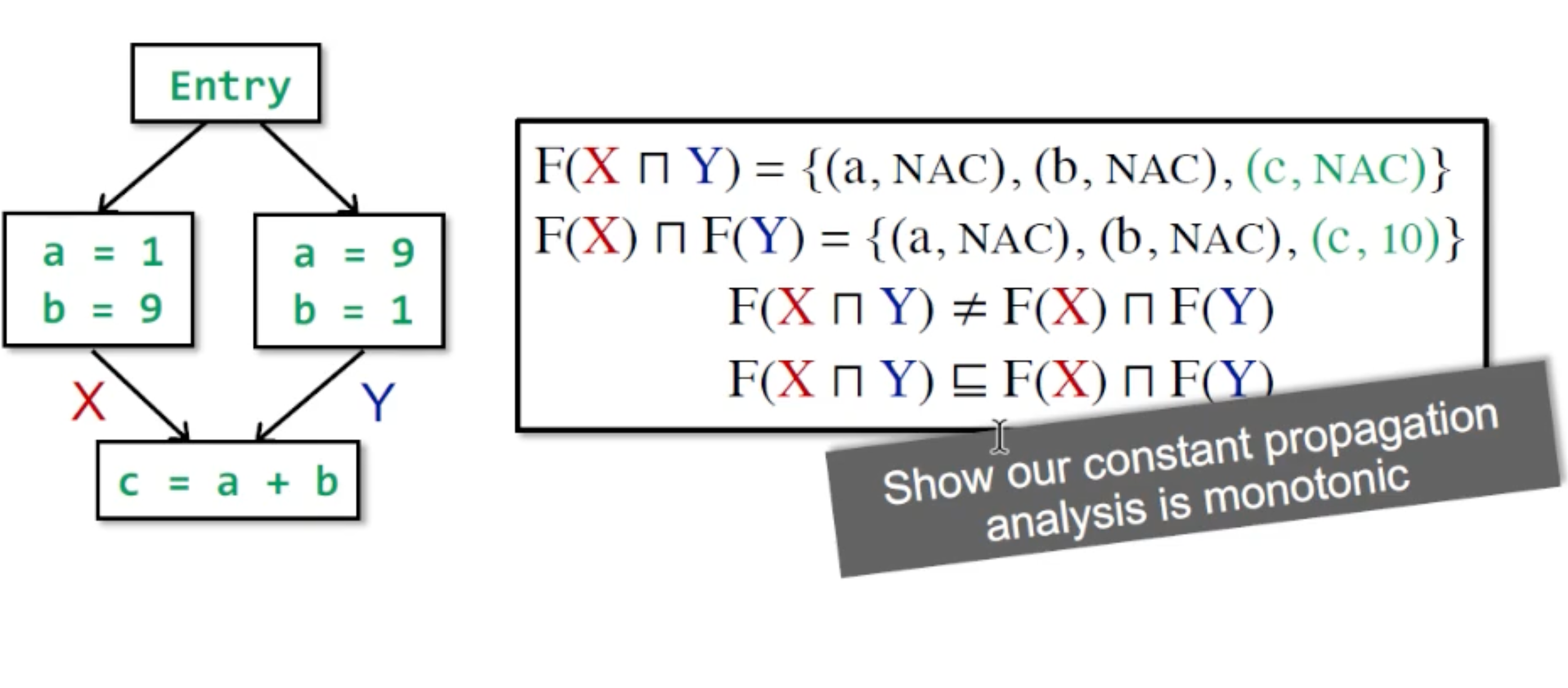
可以看到MOP在这个例子中更加准确.
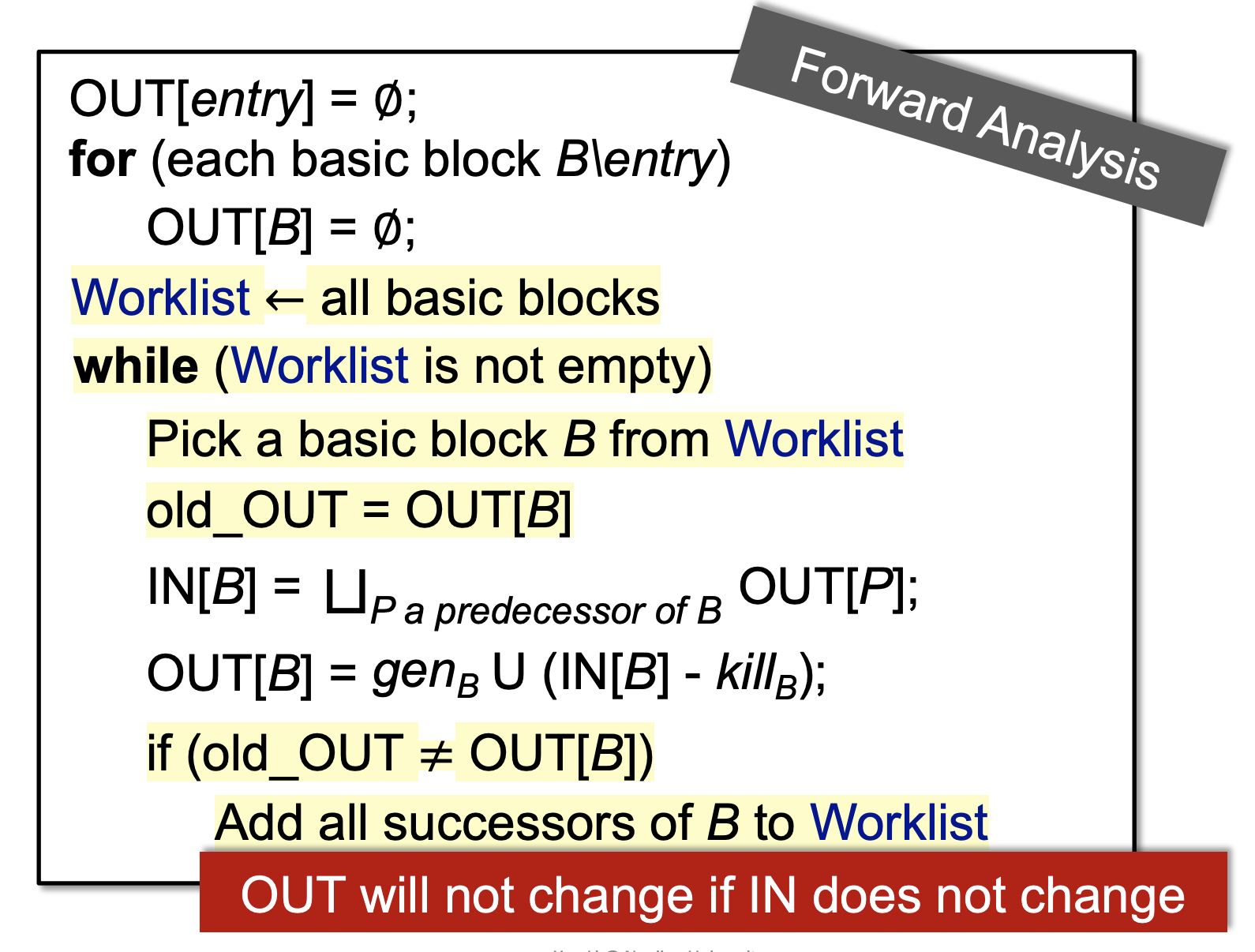
Worklist Algorithm - an optimization of Iterative Algorithm