Overview
Data Flow Analysis
→ How Data Flows on CFG?
→ How application-specific Data Flows through the Nodes and Edges of CFG
→ How application-specific Data (Abstraction) Flows (Over-approximation) through the Nodes and Edges of CFG
may analysis: outputs information may be true (over-approximation)
must analysis: outputs information must be true (under-approximation)
safe-approximation: may analysis safe=over; must analysis safe=under
→ How application-specific Data (Abstraction) Flows (Safe-approximation) through the Nodes (Transfer Function) and Edges (Control-flow) of CFG
Preliminaries of DataFlow Analysis
首先介绍程序中的输入输出状态:
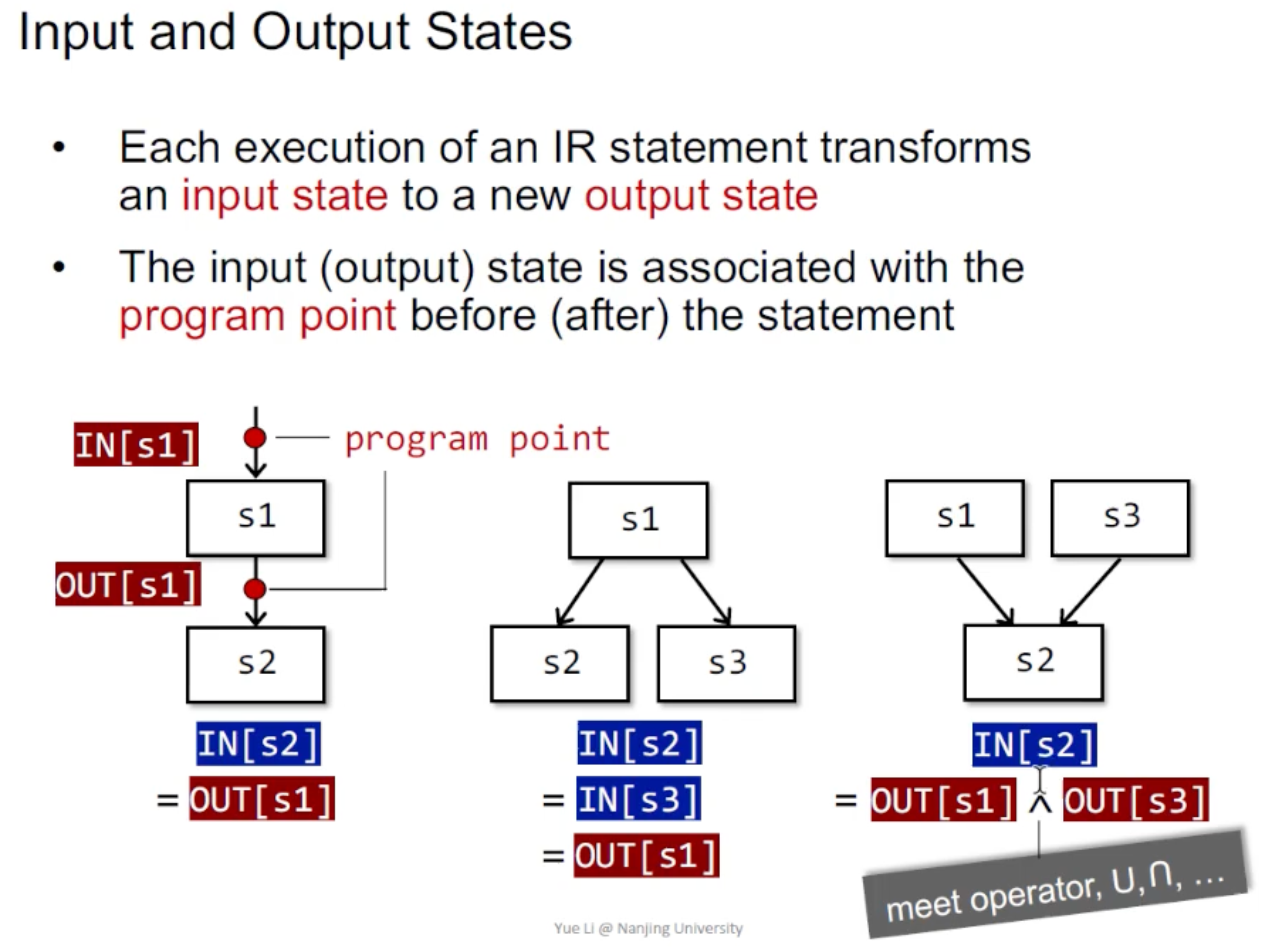
数据流分析中的最后结果应该是给每个程序中的点关联一个数据流的值 (Program state的抽象)
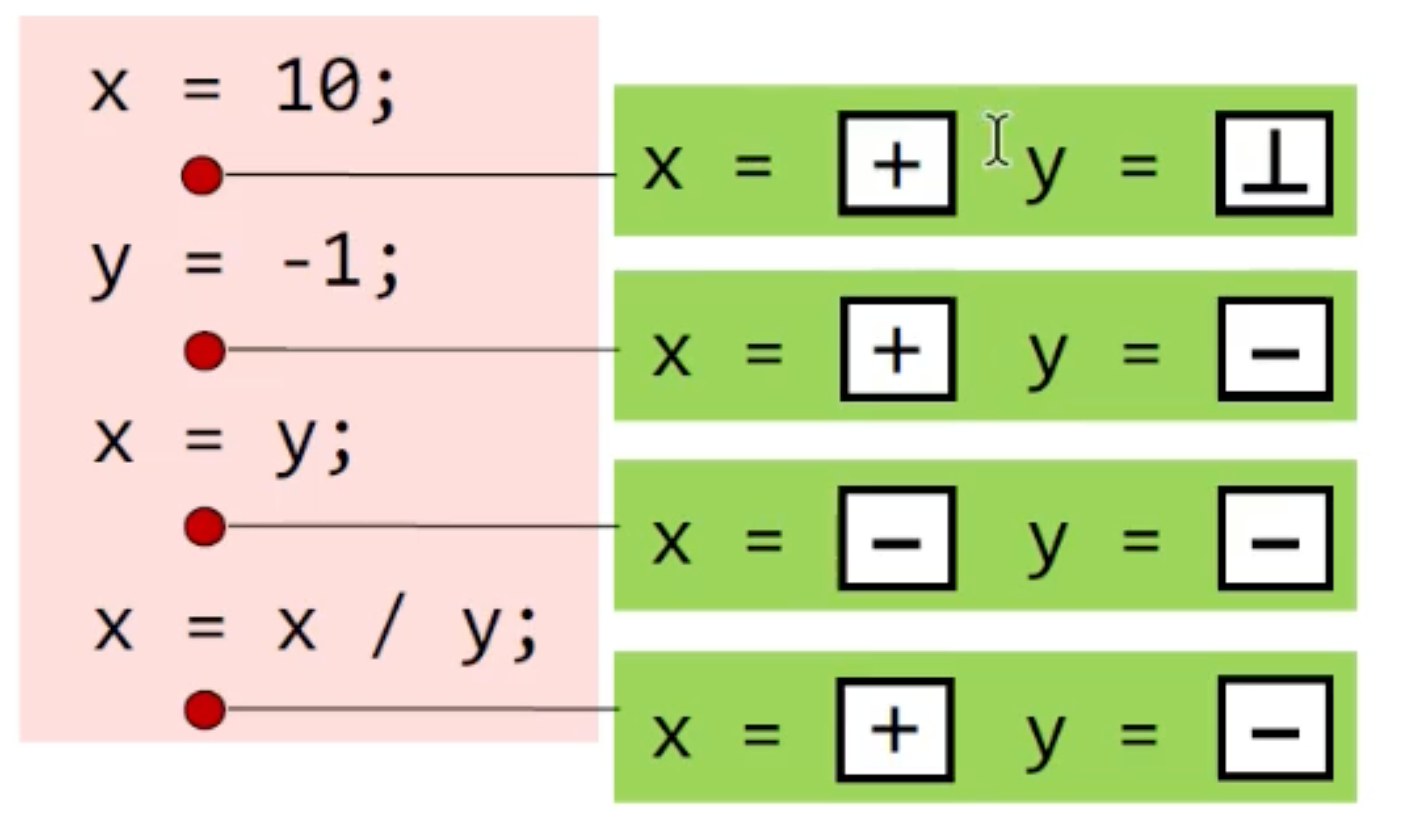
所有可能的数据流的值组成了一个集合,称为数据流的值域 (Value Domain)
数据流中状态转移有两种方式:
-
Transfer Function: Forward: OUT[s] = (IN[s]); Backward: IN[s] = f_s(OUT[s])
-
Control-flow:
-
within BB: IN[si+1] = OUT[si], for all i in 1, 2, …, n-1
-
among BBs: IN[B] = IN[s1], OUT[B] = OUT[sn]
Forward:
OUT[B] = fb(IN[B]), fb = fs1 * fs2 * … * fsn
IN[B] = a predecessor of B out[P]
Backward:
IN[B] = fb(OUT[B]), fb = fs1 * fs2 * … * fsn
OUT[B] = a succeesor of B IN[S]
Reaching Definitions Analysis
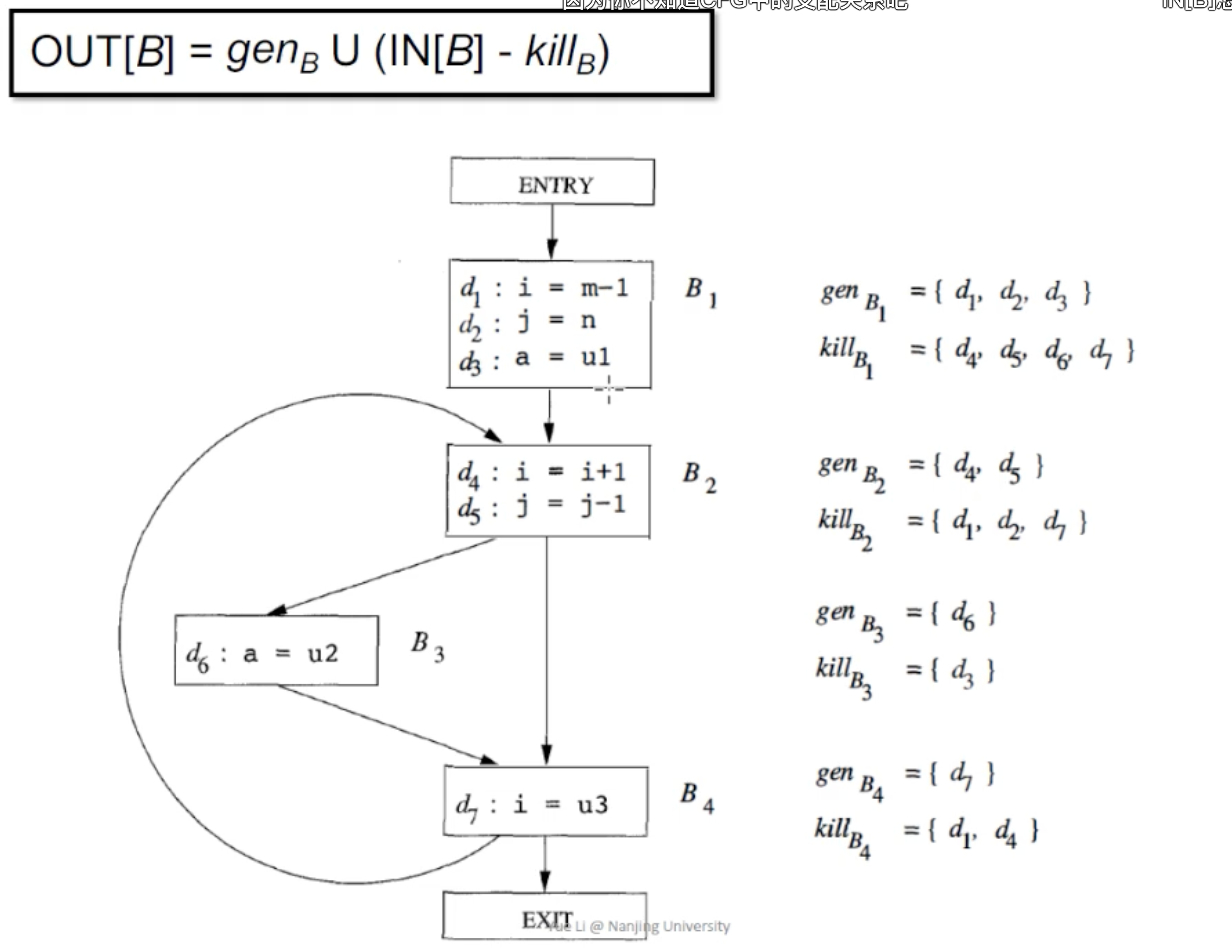
定义如下:

可用于检测undefined variables, 例如刚开始每个变量都有一个dummy definition, 如果dummy definition达到了v被使用的一点,那么就是一个undefined variable问题。
该分析是一个may analysis.
Abstraction: The definitions of all variables in the program, represented by bit vector.
Safe-Approximation:
- Transfer Function: OUT[B] = (IN[B] - )
- Control-flow:
IN[B] = OUT[P]
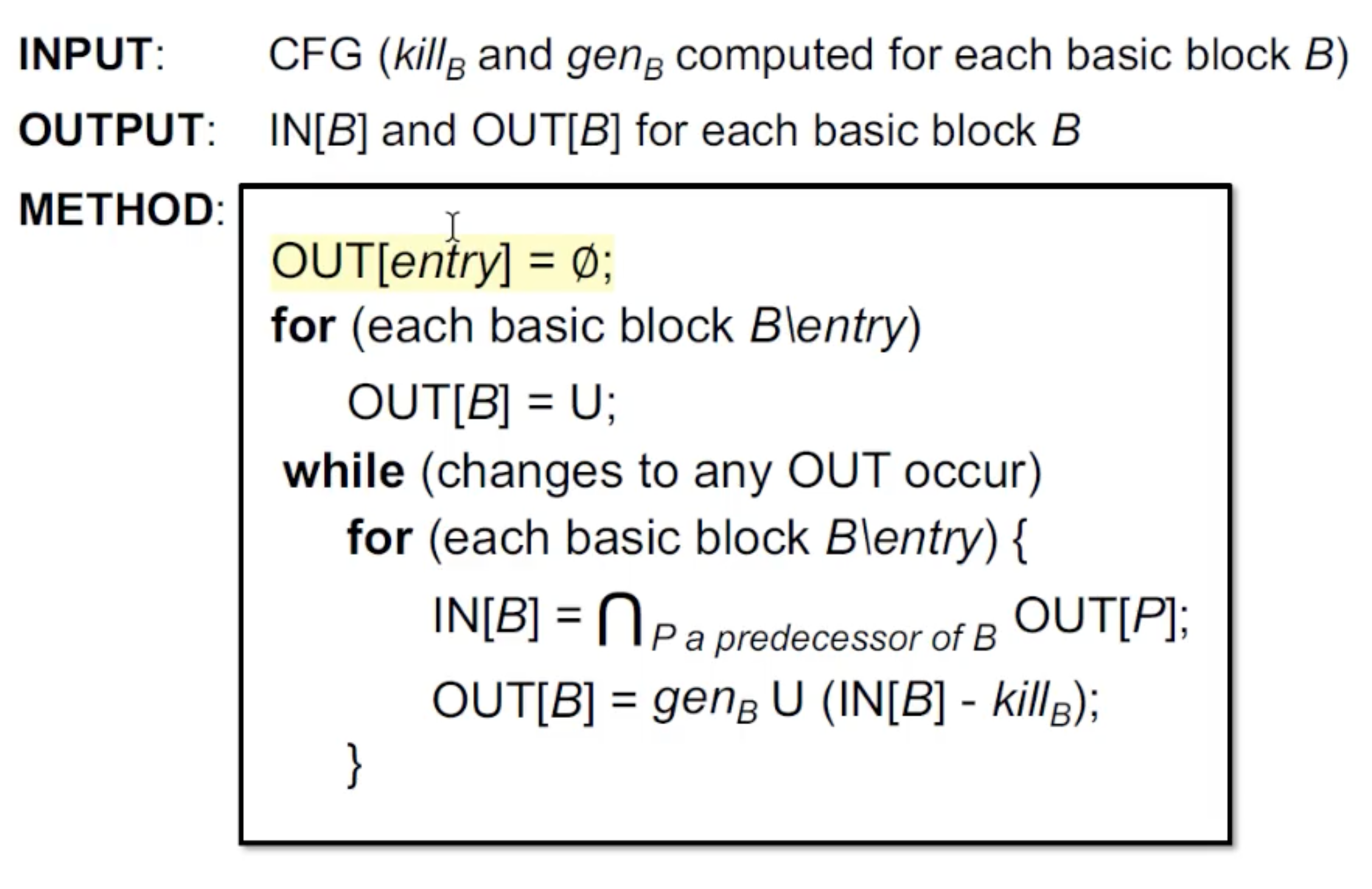
Algorithm:
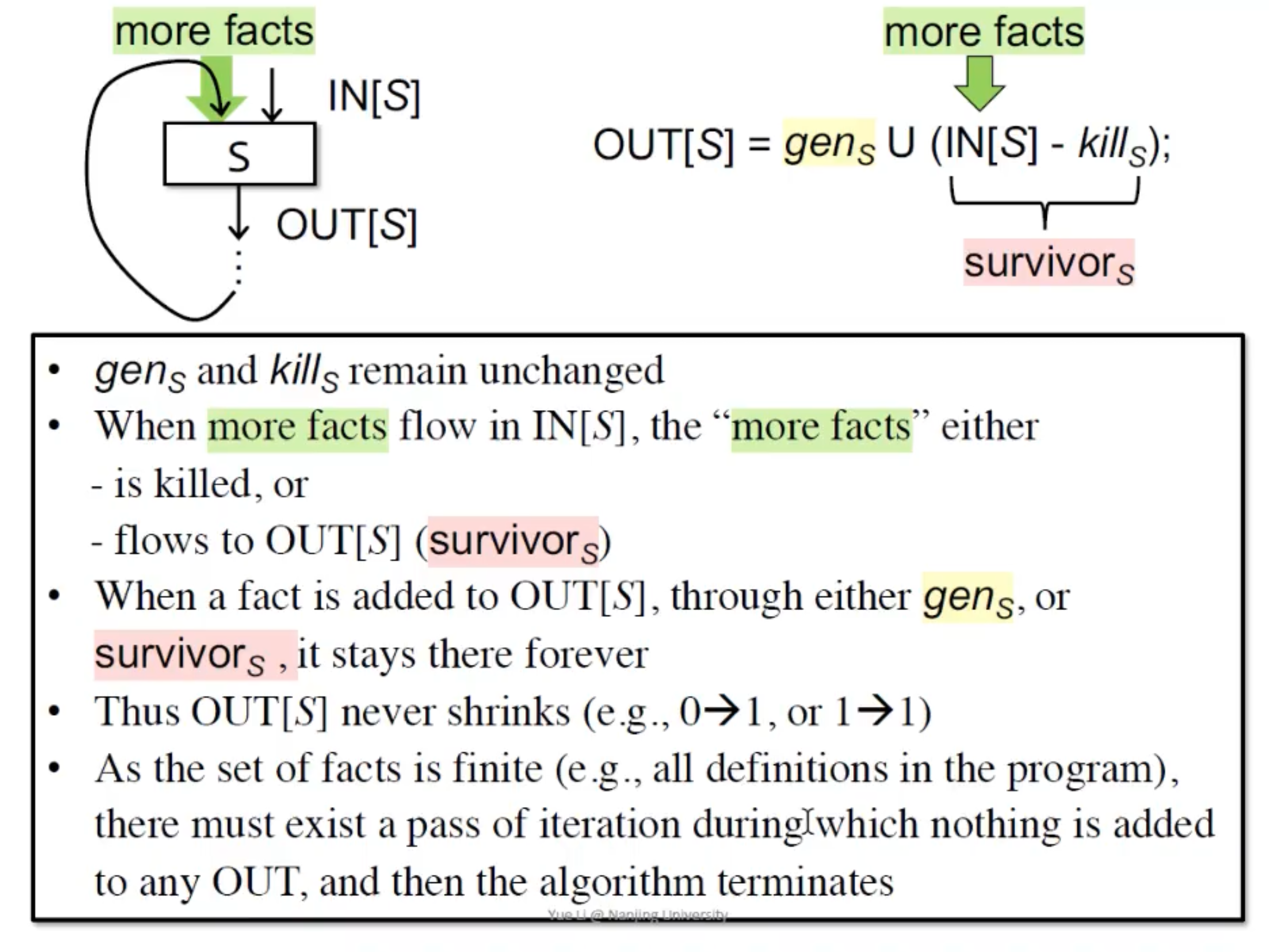
赋空的原因,目前可以理解为该分析是sound的,所以刚开始所有变量都是undefined。但实际上似乎是格上面的top和bottom的定义。
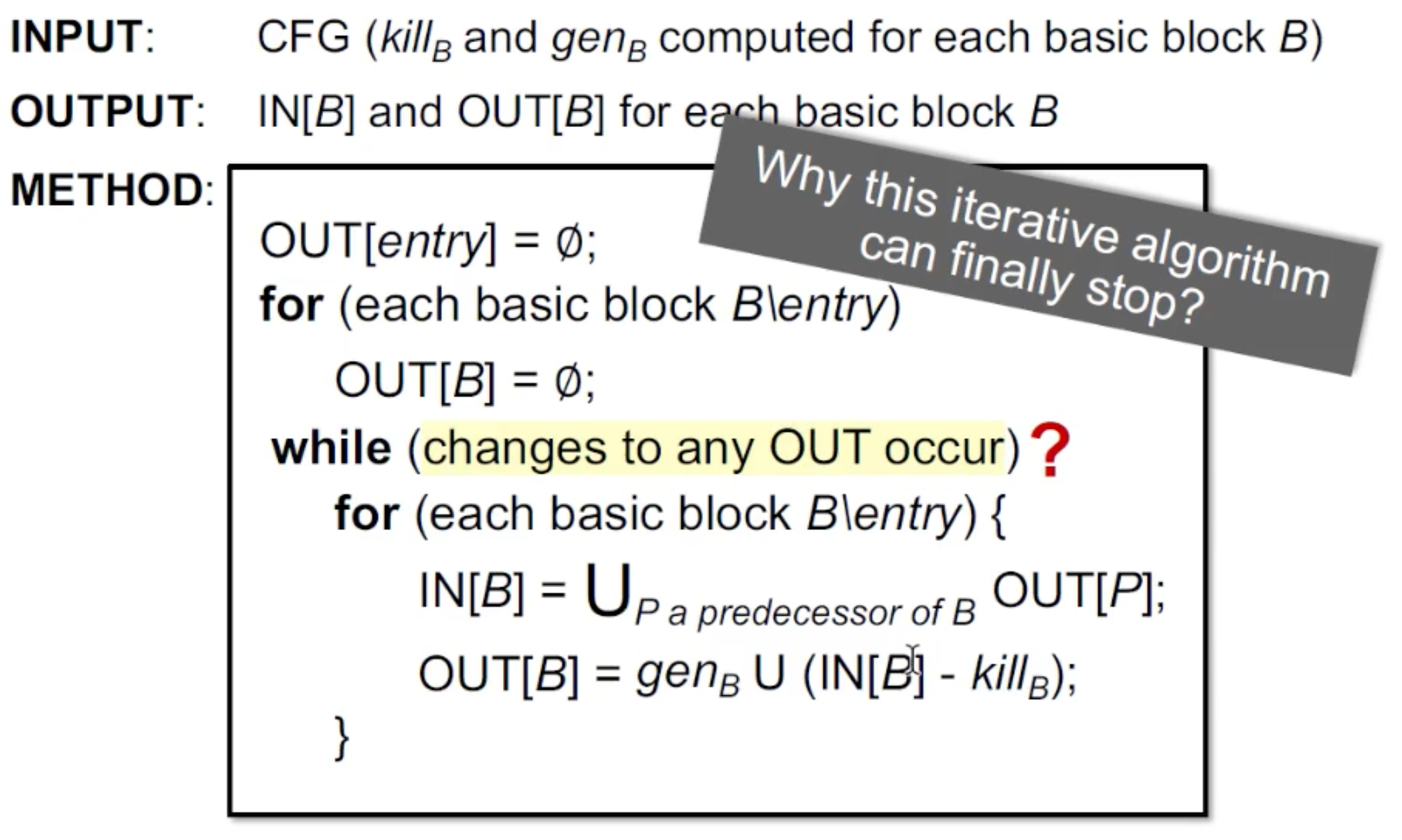
算法一定能停吗?
算法中的OUT[s]是递增的,不会缩减,而且value domain 是有限的,所以一定会停,最后会到达一个不动点。
Live Variables Analysis
同样先给该分析的定义:
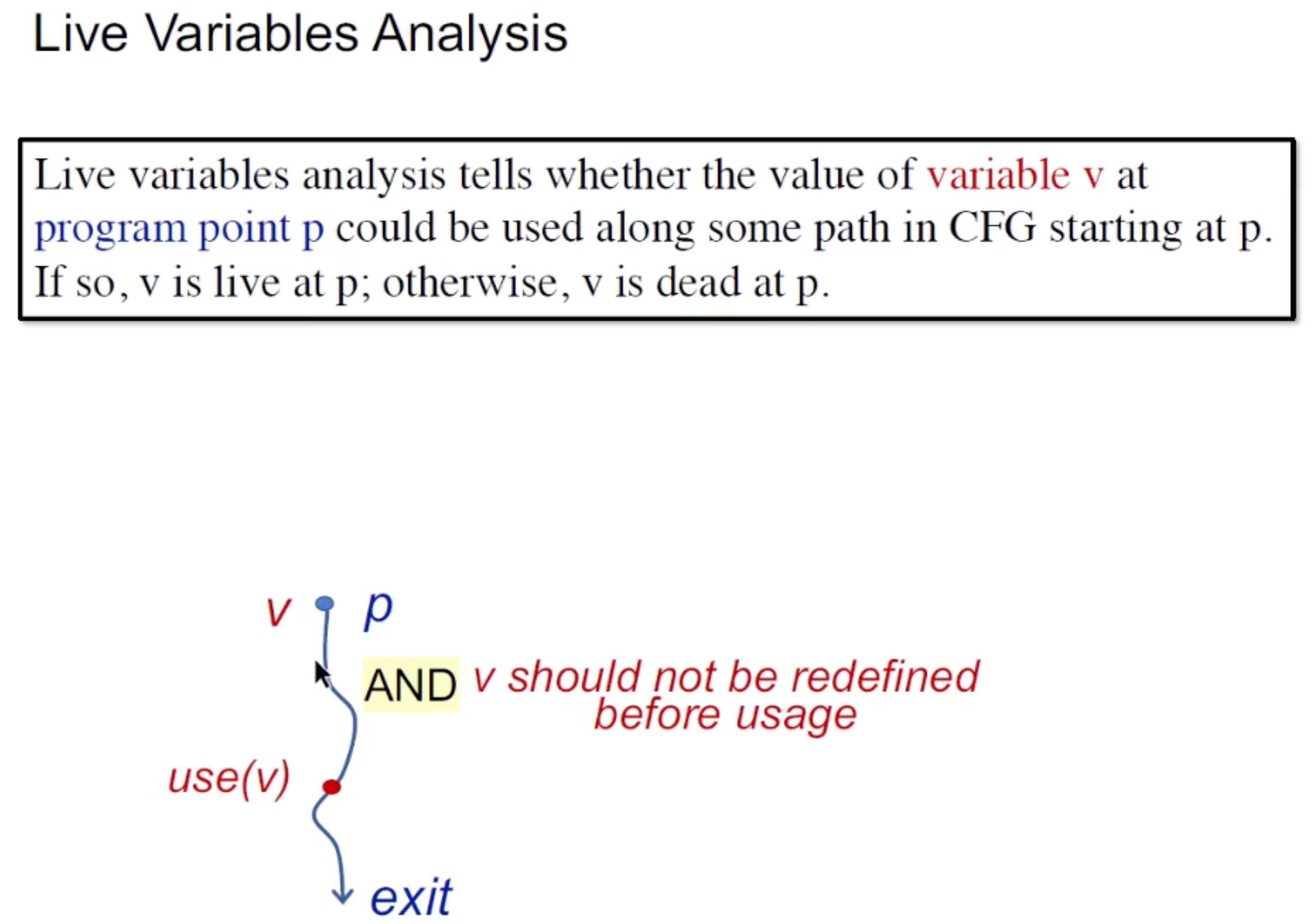
应用场景: 例如寄存器分配,当一个变量不被用之后,那么对应的寄存器就可以被释放。
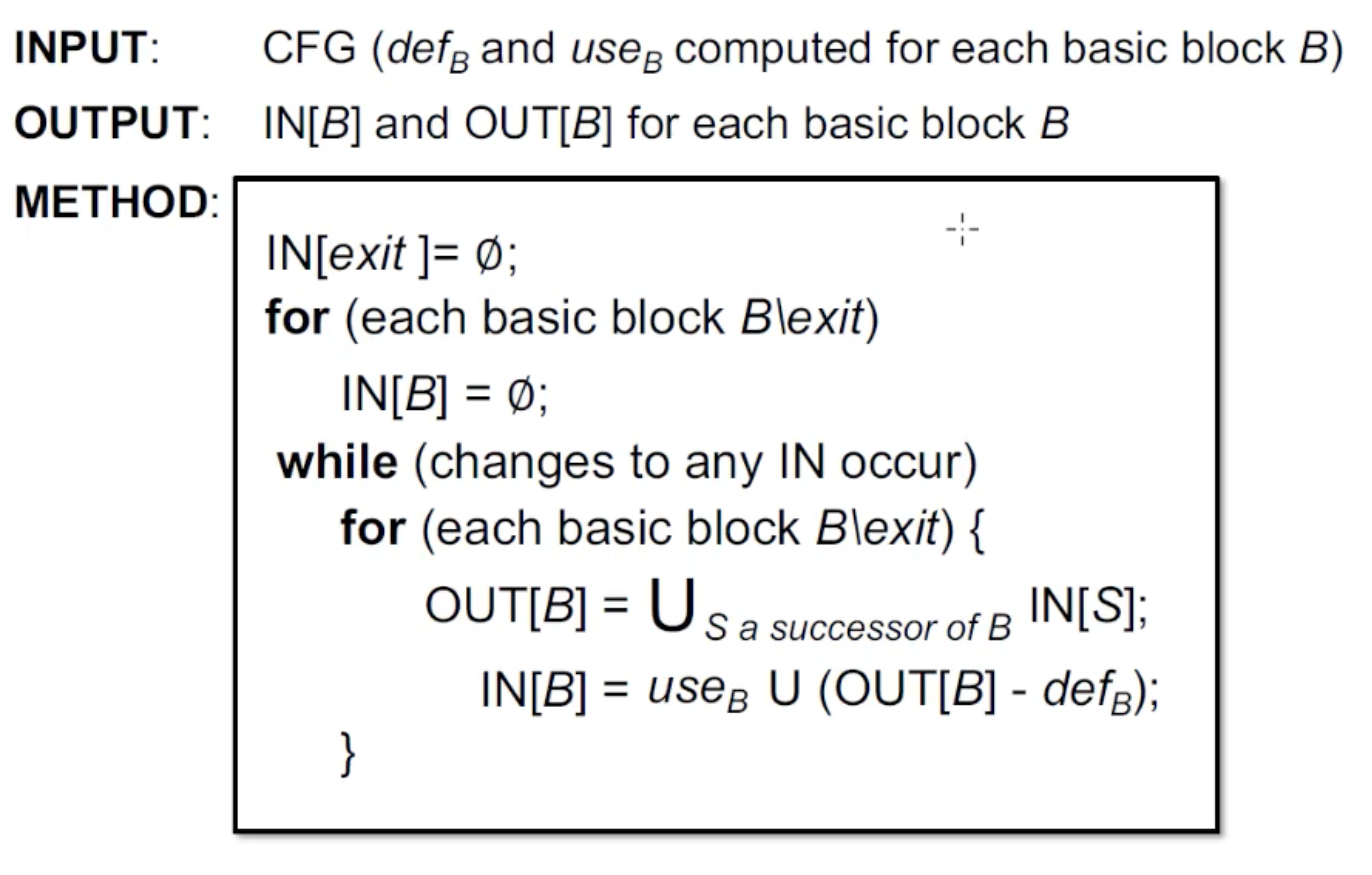
该分析也是一个may analysis, Backward analysis: 只要有一条路用了变量v,那么就可能是live的。这个live指的是stmt用了变量, 所以backward可以一遍遍历就更新.
Abstraction: All variables in the program, represented by bit vector.
Safe-Approximation:
-
Transfer Function: IN[B] = (OUT[B] - ), usage不包括define-后-use的情况。
-
Control-Flow: OUT[B] =
算法:
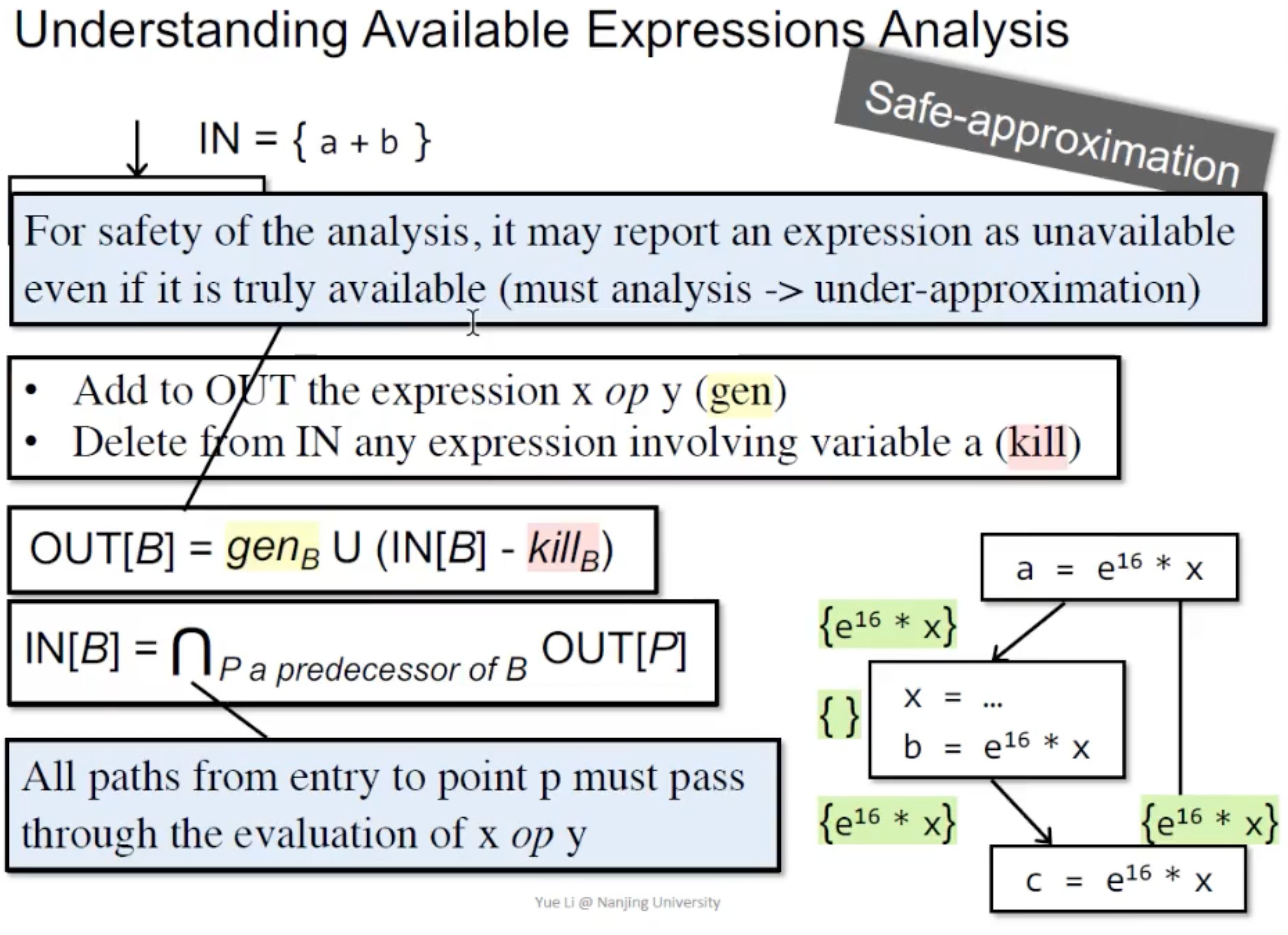
Avaiable Expressions Analysis
依旧先给定义:
从Entry到点p的,每条路径都要算x op y 而且这些路径在x op y计算之后不再重定义x或y. 可以把x op y 看作一个函数抽取出来优化程序。

This is a forward analysis.
Abstraction: 程序中所有可能的表达式,用bit vector表示。
Safe-Approximation:
Transfer Function: OUT[B] = (IN[B] - ), kill_B = expression invovle re-defined variables.
Control-Flow: IN[B] = OUT[P]
Algorithm:
每个BB的初始化是ALL,因为汇聚的时候是做交集,如果有0根本不更新。
Summary
| Reaching Definitions | Live Variables | Avaiable Expressions | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Domain | All Definitions | All Variables | All Expressions |
| Direction | Forward | Backward | Forward |
| May/Must | May | May | Must |
| Boundary | OUT[entry] = | IN[exit]= | OUT[entry] = |
| Initialization | OUT[all] = | IN[all] = | OUT[entry] = , OUT[BB] = ALL |
| Transfer Function | OUT = gen + (IN - kill) | … | … |
| Meet |